________________
JAIN JOURNAL: VOL-XLVIII, NO. 1-IV JULY 2013-JUNE 2014
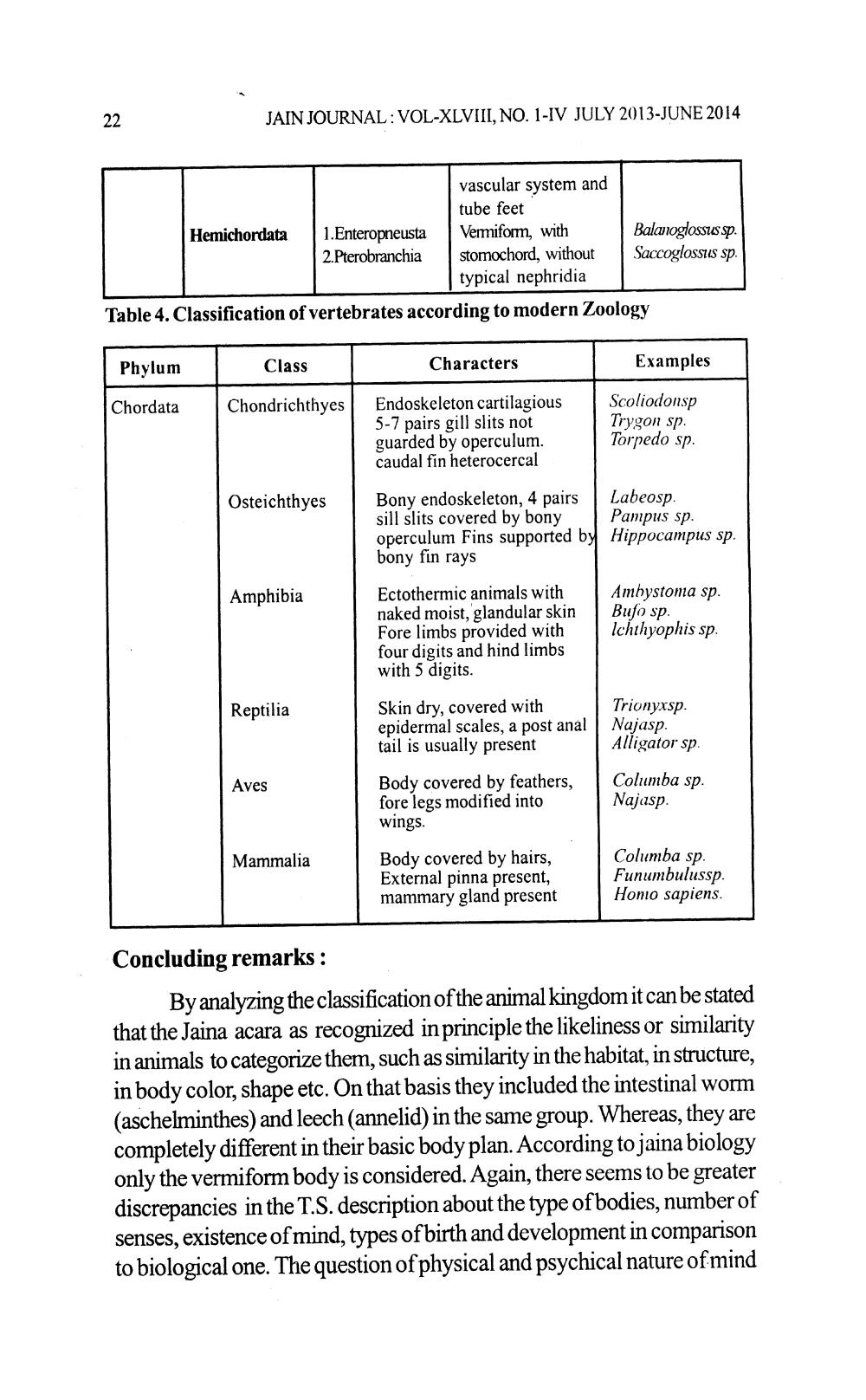
vascular system and
tube feet Hemichordata 1.Enteropneusta Vermiform, with Balanoglossus sp. 2.Pterobranchia stomochord, without Saccoglossus sp.
typical nephridia Table 4. Classification of vertebrates according to modern Zoology
Phylum
Class
Characters
Examples
Chordata
Chondrichthyes
Endoskeleton cartilagious 5-7 pairs gill slits not guarded by operculum. caudal fin heterocercal
Scoliodonsp Trygon sp. Torpedo sp.
Osteichthyes
Bony endoskeleton, 4 pairs Labeosp. sill slits covered by bony | Pampus sp. operculum Fins supported by Hippocampus sp. bony fin rays
Amphibia
Ectothermic animals with naked moist, glandular skin Fore limbs provided with four digits and hind limbs with 5 digits.
Ambystoma sp. Bufo sp. Ichthyophis sp.
Reptilia
Skin dry, covered with epidermal scales, a post anal | tail is usually present
Trionyxsp. Najasp. Alligator sp.
Aves
Body covered by feathers, fore legs modified into wings.
Columba sp. Najasp.
Mammalia
Body covered by hairs, External pinna present, mammary gland present
Columba sp. Funumbulussp. Homo sapiens.
Concluding remarks :
By analyzing the classification of the animal kingdom it can be stated that the Jaina acara as recognized in principle the likeliness or similarity in animals to categorize them, such as similarity in the habitat, in structure, in body color, shape etc. On that basis they included the intestinal worm (aschelminthes) and leech (annelid) in the same group. Whereas, they are completely different in their basic body plan. According to jaina biology only the vermiform body is considered. Again, there seems to be greater discrepancies in the T.S. description about the type of bodies, number of senses, existence of mind, types of birth and development in comparison to biological one. The question of physical and psychical nature of mind