________________
Syntropy 2013 (2): 243-279
ISSN 1825-7968
6. General Systems Theory and its implications:
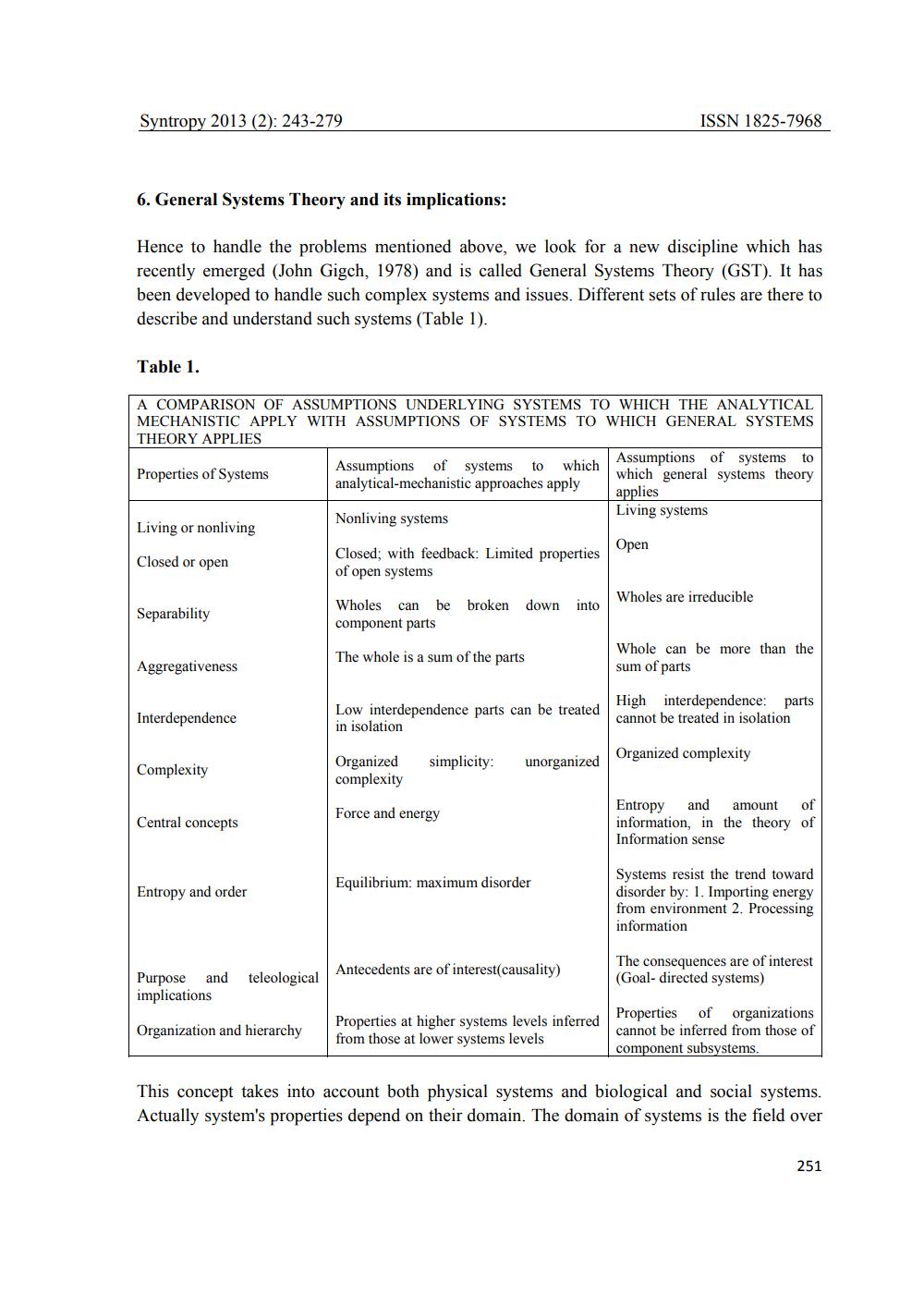
Hence to handle the problems mentioned above, we look for a new discipline which has recently emerged (John Gigch, 1978) and is called General Systems Theory (GST). It has been developed to handle such complex systems and issues. Different sets of rules are there to describe and understand such systems (Table 1).
Table 1.
A COMPARISON OF ASSUMPTIONS UNDERLYING SYSTEMS TO WHICH THE ANALYTICAL
DERLYING SEMMSTOWWIELICHEHERANALYTTE MECHANISTIC APPLY WITH ASSUMPTIONS OF SYSTEMS TO WHICH GENERAL SYSTEMS THEORY APPLIES
Assumptions of systems to Assumptions of systems to which Properties of Systems
which general systems theory analytical-mechanistic approaches apply
applies
Living systems Nonliving systems Living or nonliving
Closed; with feedback: Limited properties Closed or open
of open systems Wholes can be broken down into
Wholes are irreducible Separability component parts
Whole can be more than the The whole is a sum of the parts Aggregativeness
sum of parts
Open
Interdependence
Complexity
High interdependence: parts Low interdependence parts can be treated
cannot be treated in isolation in isolation Organized
Organized complexity simplicity: unorganized | complexity
Entropy and amount of Force and energy
information, in the theory of Information sense
Central concepts
Equilibrium: maximum disorder
Entropy and order
Systems resist the trend toward disorder by: 1. Importing energy from environment 2. Processing information
teleological
Antecedents are of interest(causality)
The consequences are of interest (Goal-directed systems)
Purpose and implications
Organization and hierarchy
Properties at higher systems levels inferred from those at lower systems levels
Properties of organizations cannot be inferred from those of component subsystems.
This concept takes into account both physical systems and biological and social systems. Actually system's properties depend on their domain. The domain of systems is the field over
251